
Sickle cell anemia
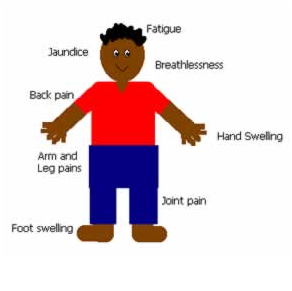
Sickle cell anemia is a disease in which your body produces abnormally shaped red blood cells. The cells are shaped like a crescent or sickle. They don't last as long as normal, round red blood cells. This leads to anemia. The sickle cells also get stuck in blood vessels, blocking blood flow. This can cause pain and organ damage. A genetic problem causes sickle cell anemia. People with the disease are born with two sickle cell genes, one from each parent. If you only have one sickle cell gene, it's called sickle cell trait. The most common symptoms are pain and problems from anemia. Anemia can make you feel tired or weak. In addition, you might have shortness of breath, dizziness, headaches, or coldness in the hands and feet. A blood test can show if you have the trait or anemia.
Sickle cell anemia has no widely available cure. Treatments can help relieve symptoms and lessen complications.Such treatment includes hydroxyurea, penicillin prophylaxis, immunization, and blood transfusions when required. Researchers are investigating new treatments such as blood and marrow stem cell transplants, gene therapy, and new medicines.
We now know a lot about how sickle cell anemia causes bone and organ damage and treatment measures to prevent these crises are very helpful in keeping patients well and healthy for longer periods of time.

